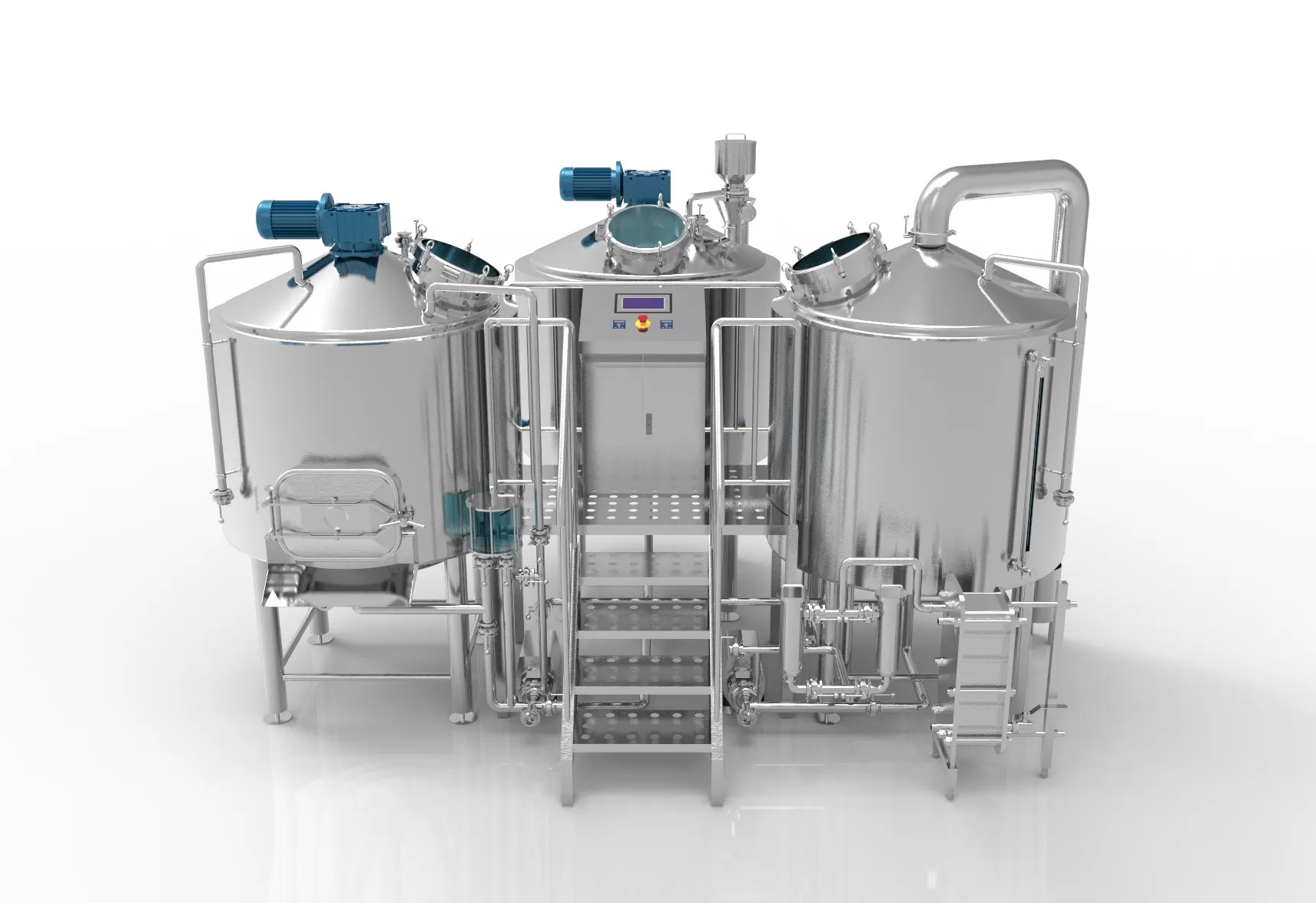
Craft beer is an exact science. Brewers know that different types of yeast and different fermentation methods control the taste of beer. But a phenomenon known as “hop creep” can sometimes get brewers into trouble. Jumping Creepy isn’t an outdoor children’s game, nor is it an obnoxious character lurking around a bar. Hop creep is a common term that refers to the over-fermentation of dry-hopped hops. As dry hopping becomes a process step in breweries, and the average number of hops per dry hop increases, this phenomenon is detrimental to brewing results.
ジャンプクリープとは何か?
ホップクリープとは、ホップに含まれるアミロ分解酵素によってドライホップビールの発酵が促進されること。これらの酵素は非発酵性デキストリンをマルトトリオース、マルトース、グルコースなどの短鎖オリゴ糖に分解する。酵母は長鎖デキストリンをどうするか知らないが、グルコースとマルトースを発酵させることができる。
セカンダリー期間中 発酵, the remaining yeast cells in the new beer convert these sugars into alcohol, carbon dioxide, and secondary metabolites, which are unwanted fermentation intermediates. The term “hop creep” was coined by American craft brewers because it is a hidden, slow process that can cause brewers unpleasant surprises. This phenomenon is now the subject of research.

すべてのホップがホップクリープを引き起こすのか?
異なるホップ品種は可溶性デンプン溶液で性能を発揮するが、実際のドライホッピング試験でも性能を発揮する。2018年にJournal of the American Society of Brewing Chemistsに掲載された論文によると、その理論はまだ証明されていないが、ホップの遺伝はその活性に影響を与えるようで、Amarillo®とCascadeは他の品種よりもアルコールや濃度レベルを変化させると説明されている。シムコー®、センテニアル、そしてシトラ®。とはいえ、植物や球果の成熟度(年齢ではない)、栽培条件、収穫時や収穫後の取り扱いや加工が、それぞれの品種のホップのクロール活性に影響を与える。
ホップクリープの影響は?
ホップクリープとは、ビールに残ったドライホップを別の方法で再発酵させること。ドライホップの発酵中に、ホップ関連の酵素が一次発酵で残った発酵不可能なデキストリンを分解し始める。出来上がったビールに残った酵母は、放出された糖を代謝し、アルコールと二酸化炭素を生成する。
- 活性酵母は新しい発酵可能な糖を代謝し、より多くのアルコールを生産する。余分なアルコールによる風味への影響。季節外れのビールは捨ててもよい。
- 活性酵母は新しい発酵可能な糖を代謝し、より多くの二酸化炭素を生成する。パックビール中の過剰な炭酸ガスは、過炭酸の原因となります。さらに、圧力の上昇により容器が破裂することもあります。
- 活性酵母は発酵中にアセト乳酸を分泌し、これが酸化されてジアセチル化合物を形成する。ビールはバターやバタースコッチのような味がする。一般的に、ジアセチルはほとんどのビールスタイルにおいて、特に多量に存在する場合には欠陥とみなされる。
ホップクリープの原因は?
Before we jump straight into managing jump creep, let’s discuss some of the factors that influence jump creep. To reiterate the obvious, hop creep only occurs when beer is dry-hopped. Many of the dry hop factors that affect flavor and aroma also affect hop creep:
- 時間:ホップとビールを混ぜる時間が長いほど、ホップの酵素が一次発酵で残ったデキストリンを分解できる。
- 温度:一般的に、温度が高いほどイーストの発酵活性は高くなる。また、温度が高いと不健康な酵母が再び発酵を始める可能性がある。
- ホップの量:ホップの量が多いほど、デキストリンを分解する酵素の量も多くなる。
- Hop processing: Before hops are distributed to the brewery, they undergo a dehydration or “drying” process. This process prevents the hops from spoiling during distribution and storage. The hops producer will heat the hops. If the heat is high enough and applied for the right time, most of the enzymes responsible for hop creep will denature.
- ホップ品種:ホップ品種によって油分の含有量や成分が異なるため、酵素活性もホップ品種によって異なる。
- ビールそのもの:残糖を多く含むビールをドライホッピングすると、やがてホップのクリープから発酵可能な糖が多く生成される。

ホップのクリープを防ぐには?
ホップ・フォーム
Carbon dioxide extract and cryogenic pellets are less likely to cause hop creep. Whole cone hops are more likely to cause hop creep because the enzyme in question is believed to be involved in the hops’ green stuff, which is more prevalent in whole cones.
ドライホップの持続時間
ドライホップの持続時間を短くすることで、ホップクリープの影響と可能性を減らすことができる。
ドライホップの温度
ドライホップの温度は、ホップクリープを軽減または防止するために10℃以下を推奨します。ドライホップの温度が高いとクリープが発生しやすくなります。
ドライホップの量
ホップクリープを抑えるため、ドライホップの使用量は少なめ(1バレルあたり2ポンド以下、または約6.5グラム/リットル)にすることを推奨する。ドライホップの使用量が多いと、ホップクリープのリスクや程度が高まる可能性がある。
発酵酵母の負荷
Hop creep can only occur with active yeast in the beer suspension – the more yeast there is in the suspension, the greater the potential for hop creep when dry hops are added.
包装用酵母の存在
ホップのクリープは、包装前にビールから酵母を取り除けば防ぐことができる。これは家庭で醸造するレベルでは不可能かもしれませんし、霞がかかったような商業的なタイプのビールなどでは、ホップの存在は必要です。