Plate heat exchangers and shell and tube heat exchangers are the two most common types of heat exchangers, and they both serve a lot when you want to heat or cool wort during processing. In the new era of sustainable development, saving energy and reducing environmental impact is becoming more and more urgent. By using a plate heat exchanger, energy can be transferred between two fluids at different temperatures. This improves efficiency through heat transfer.
What is a heat exchanger?
A heat exchanger is an electrical circuit element that provides heat transfer (without mixing with each other) between two fluids (liquid or gas) having a temperature difference without any physical contact.
Heat exchangers are in principle divided into three types:
– Tubular heat exchanger
– Plate heat exchanger
– Special application heat exchangers

Type of heat exchanger
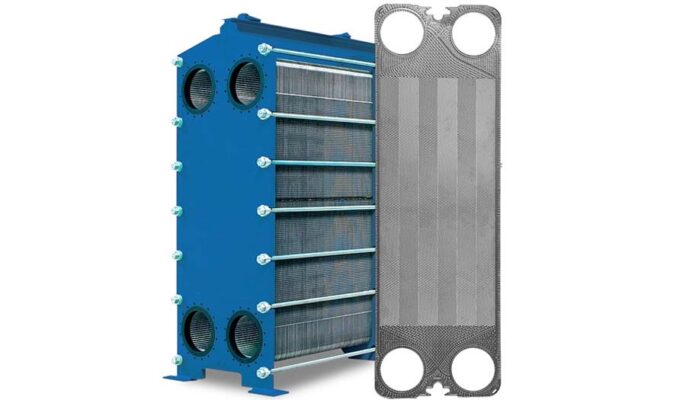
If you have been exposed to liquid cooling products before, you will encounter two options: shell and tube heat exchanger and plate heat exchanger. Shell and tube and plate heat exchangers work on the same principle, exchanging heat between two fluids by conduction, but are constructed in very different ways.
Shell and tube heat exchanger
Consisting of a bundle of small tubes within an outer shell, a shell and tube heat exchanger is a simple but effective construction. The principles have been around for a long time. Due to their simplicity and flexibility, they can be manufactured at low cost, even in small quantities. They are ideal for applications that must regular maintenance and maintenance.
Plate heat exchanger
A heat exchanger, a brewery piece of equipment designed to raise or lower the temperature of wort or beer. Heat exchangers in breweries are often referred to as “plate heat exchangers” because they consist of a series of plates. Hot liquid flows along one side of the plate and cold liquid flows along the other side of the plate. Heat exchange occurs between the plates. The most common heat exchangers are located in breweries. The hot wort at approximately 95°C flows through the heat exchanger and is cooled by cold water and refrigerant flowing in the opposite direction along the opposite side of the plates.
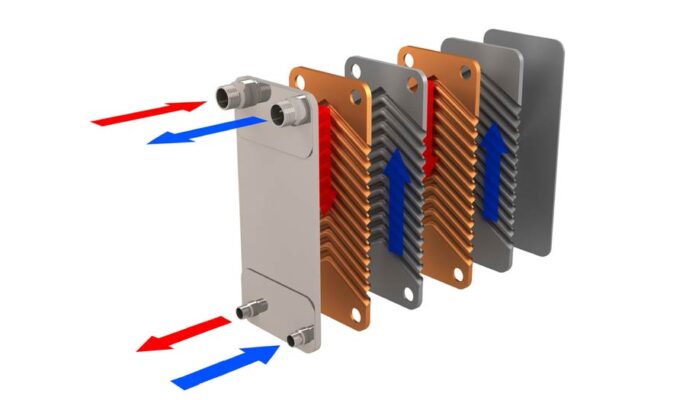
Plate heat exchanger and shell and tube heat exchanger
Compared with shell and tube heat exchangers, plate heat exchangers have several unique advantages.
- Expandability: Plate heat exchangers usually have extra space in the frame.
- More convenient maintenance: the plate heat exchanger can be opened for inspection and maintenance. You can also replace damaged boards.
- Efficiency: Variable pressing depth and large heat exchange surface area provide efficient thermal performance and controlled heating and cooling.
Benefits of Plate Heat Exchangers
- Higher temperature capability
- Low heat loss
- Compact structure, saving space
- It is convenient to change the heat transfer area
- Easy to clean and maintain
- Wide range of applications
- Long service life
- Ideal for small district heating, beverage cooling, food and pharmaceutical production, and low load oil cooling applications
Disadvantages of plate heat exchangers
- low working temperature
- More maintenance costs due to gaskets
- Not suitable for products with very high viscosity or very large particles
Advantages of shell and tube heat exchangers
- Smaller design can reduce cost
- Service becomes easier
- O-ring maintenance costs are low
- Better solution for seawater coolant or other liquids that may clog tight spaces
- Provide better installation options
- The ideal solution for hydraulic power units, mining machinery, seawater cooling vessels and swimming pool heating
Disadvantages of shell and tube heat exchangers
- Takes up a lot of space
- Difficult to clean and maintain
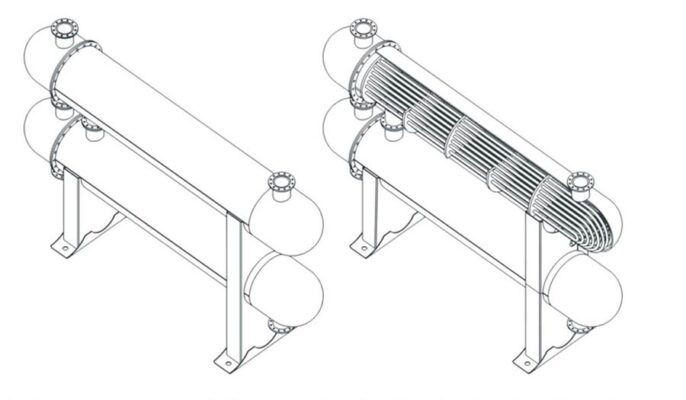
Plate Heat Exchanger Structure
In these exchangers, each plate has a confined concave tubular casing. The plates are arranged in such a way on form thin rectangular channels to divert heat through the part.
Working fluid flows between these twisted and narrow channels. Gaskets surround the plates of the exchanger to control fluid flow. These gaskets are arranged in such a way that only one type of fluid is distributed on one plate, while the other fluid is distributed on the upcoming plate.
Cold fluid and hot fluid pass through the plates, whereby heat exchange takes place. Plates have a larger surface area, so, they have superior heat transfer rates than tubular heat exchangers.
Important Benefits of Using a Heat Exchanger
Smaller Space Footprint
With the advancement of modern technology, it seems that more powerful also means smaller. Smaller personal devices, smaller, more general-purpose manufacturing equipment, and more. Shrinking space in electrical cabinets increases the risk of hot spots and damage to electrical components, which increases the need for smaller, more efficient cooling solutions.
Reduce environmental impact
To function, the heat exchanger must run to ensure that the high-power control panel does not overheat. One of the greatest benefits of modern heat exchangers is that they do not rely on more equipment to operate. As a result, they use less energy and produce little or no pollution compared to more traditional cooling methods.
Lowest operating cost
Heat exchangers use no complicated external equipment and are designed to cut most contamination. Doesn’t must as much maintenance as an air conditioner.




